A) heterozygous.
B) homozygous dominant.
C) homozygous recessive.
D) a clone of the other test cross individual.
E) heterozygous recessive.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Homologous chromosomes have
A) the same genes but can have different alleles.
B) the same genes and alleles.
C) different genes and alleles.
D) different genes, but can have the same alleles.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The alleles of each gene packaged into separate gametes summarizes Mendel's law of
A) segregation.
B) random fertilization.
C) population dynamics.
D) crossing over.
E) independent assortment.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genotype means the
A) number of gametes in an individual.
B) combination of alleles in an individual.
C) number of chromosomes in an individual.
D) observable expression of the genes in an individual.
E) genes an individual has.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Traits that depend on more than one gene are
A) polygenic.
B) pleiotropic.
C) codominant.
D) recessive.
E) incomplete dominant traits.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A recessive allele is one whose effect is masked if a dominant allele is also present.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "P" in "P generation" refers to
A) pure breeding.
B) parental.
C) potential offspring.
D) recessive allele.
E) All answers are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The individual sometimes referred to as the "father of genetics" because he influenced the science of genetics more than anyone else is Gregor Mendel.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pea plant (Pisum sativum) is a good choice for studying heredity because it
A) develops slowly.
B) produces only a few offspring.
C) is easy to control which plants mate with each other.
D) has only a few traits that appear in two easily distinguishable forms.
E) All answers are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The most common allele for any trait is always the dominant allele.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Mendel crossed tall (Tt) plants with tall (Tt) plants the offspring
A) did not grow and reproduce.
B) were always short.
C) were always tall.
D) were always medium height.
E) were mostly tall individuals and a few short individuals.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Having the alleles Tt is
A) a phenotype.
B) linkage.
C) a genotype.
D) a gene.
E) a locus.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The environment only rarely affects gene expression.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In these data, the parental generation characteristics (resistant or susceptible) are shown at the top.
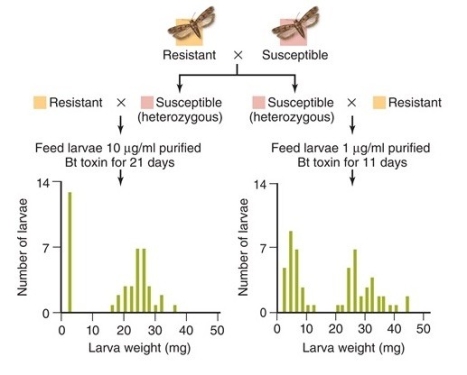 -The F₂ generation (the larvae measured in comparison) is shown in the graphs at the bottom of this figure.The cluster of bollworms at lower larva weights would have which genotype?
-The F₂ generation (the larvae measured in comparison) is shown in the graphs at the bottom of this figure.The cluster of bollworms at lower larva weights would have which genotype?
A) RR
B) rr
C) Rr or RR
D) Rr
E) Rr or rr
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diagrams of gene order and spacing on chromosomes are
A) genotypes and phenotypes.
B) phenotypes.
C) linkage maps.
D) genotypes.
E) metabolic maps.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common allele,genotype,or phenotype in a population is referred to as the
A) wild type.
B) dominant population.
C) recessive population.
D) P generation.
E) F1 generation.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an individual is homozygous for a particular trait
A) each parent contributed a different allele for that trait.
B) one parent contributed two different alleles for that trait.
C) each parent contributed the same allele for that trait.
D) one parent contributed two copies of the same allele for that trait.
E) a mutation must have occurred.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an individual is heterozygous for a particular trait
A) each parent contributed a different allele for that trait.
B) each parent contributed the same allele for that trait.
C) one parent contributed two different alleles for that trait.
D) one parent contributed two copies of the same allele for that trait.
E) a mutation must have occurred.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans,alleles for a gene locus on autosomes are inherited from
A) females only (mothers) .
B) males only (fathers) .
C) males and females (one allele from each parent) .
D) males and females (two alleles from each parent) .
E) No answer is correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Uncorrected sequence mistakes during meiosis will lead to
A) production of only autosomes with mutations.
B) production of only sex chromosomes with mutations.
C) no living offspring.
D) no change.
E) production of gametes with mutated genes.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 94
Related Exams