A) Bad Debt Expense
B) Accounts Receivable
C) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
D) Notes Receivable
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On the maturity date of a $5,000,3-month,10% note,the borrower sends a check that includes the principal and all of the interest due on the note.What is the amount of the borrower's check?
A) $5,125
B) $5,500
C) $6,500
D) $5,000
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bolster Soda had an accounts receivable turnover ratio of 9.9 this year and 11.0 last year.Castor Soda had a turnover ratio of 9.3 this year and 9.3 last year.This implies:
A) Castor's receivables turnover ratios were better than Bolster's for both years.
B) Bolster's receivables turnover ratios were better than Castor's for both years.
C) Castor has credit policies that need to be tightened.
D) Castor collected receivables more quickly than Bolster in both years.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The adjusting entry to record the estimated bad debts in the period credit sales occur would normally include a debit to:
A) Accounts Receivable and a credit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
B) Bad Debt Expense and a credit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
C) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and a credit to Accounts Receivable.
D) Bad Debt Expense and a credit to Accounts Receivable.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The receivables turnover ratio:
A) is calculated as the average number of days from the time a sale is made on account to the time cash is collected.
B) is calculated as the average number of days from the time a sale is made on account to the time payment is due.
C) measures how many times a year receivables go uncollected.
D) measures how many times, on average, the process of selling and collecting is repeated during the period.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Samberg Inc.had the following transactions. Oct.1 - Sold $10,000 of merchandise on account,1/10,n/30 to McCormick Industries. Nov.1 - Received a $10,000,90-day,10% note from McCormick Industries to settle its $10,000 unpaid balance. Dec.31 - Accrued interest on the note.(Round to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Jan.31 - Received the interest on the note's maturity date. Jan.31 - Received the principal on the note's maturity date.(Round to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Required: Prepare the required journal entries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The accounts receivable account for each customer is called a subsidiary account.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the allowance method,which is the correct adjusting journal entry to record bad debt expense?
A) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
B) Debit Allowance for Bad Debt Expense and credit Bad Debt Expense
C) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Sales Revenue
D) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Accounts Receivable
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The accounting principle that governs the recording of bad debt expense in the same period as sales revenue is called the:
A) expense recognition principle ("matching")
B) time period assumption
C) revenue recognition principle
D) separate entity assumption
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts on January 1 equals $10,000 and during the year $11,000 of specific customers' accounts were written off,then its Allowance for Doubtful Accounts will have an unadjusted balance of:
A) $1,000 credit
B) $1,000 debit
C) $10,000 credit
D) $9,000 debit
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A company reported a receivables turnover ratio of 8.0.Cost of goods sold was $350,000 and net sales revenue was $480,000.The average net receivables must have been
A) $45,000
B) $120,000
C) $60,000
D) $90,000
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the end of the period,the manager of Philly Electronics estimated that $40,000 of its accounts receivable were uncollectible.If the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of $11,200,which of the following sets forth the adjusting entry to record bad debts for the period?
A) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Accounts Receivable for $40,000
B) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts for $28,800
C) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts for $40,000
D) Debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Accounts Receivable for $28,800
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The entry to record the collection of a previously written-off account needs to be recorded because a customer paid $9,600 after its accounts receivable had been written off.This entry includes a:
A) debit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts of $9,600
B) debit to Bad Debt Expense of $9,600
C) credit to Bad Debt Expense of $9,600
D) credit to Allowance for Doubtful Accounts of $9,600
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The direct write-off method is not allowed under GAAP because it violates the:
A) cost principle
B) revenue recognition principle
C) sales method
D) expense recognition principle ("matching")
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Labrador Inc.has the following information available for the current year:
 What was the amount of write-offs during the year?
What was the amount of write-offs during the year?
A) $62,000
B) $0
C) $55,000
D) $40,000
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wadsworth Corp.has the following information:
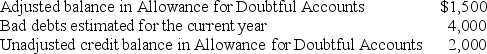 No recoveries were recorded during the year.What was the amount of accounts written off during the year?
No recoveries were recorded during the year.What was the amount of accounts written off during the year?
A) $7,500
B) $4,500
C) $4,000
D) $2,000
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the aging method of accounts receivable method,$5,000 of the company's Accounts Receivable are estimated to be uncollectible.At the end of the year,the balance of Accounts Receivable is $100,000 and the unadjusted credit balance of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is $500.Credit sales during the year totaled $150,000.What is the current year's Bad Debt Expense?
A) $4,500
B) $5,000
C) $7,000
D) $7,500
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The adjusting entry used to record the estimated bad debts in the period credit sales occur decreases:
A) both net income and net accounts receivable.
B) net income and increases liabilities.
C) assets and increases liabilities.
D) both selling expenses and net income.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Davidoff Company reported net credit of $735,000 on account for the year ending December 31,2016.On January 1,2016,the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts had a credit balance of $18,000.During 2016,$30,000 of uncollectible accounts receivable were written off.Davidoff has experienced bad debt losses of 3% of credit sales in prior periods.Using the percentage of credit sales method,what is the adjusted balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December 31,2016?
A) $10,050
B) $10,500
C) $22,050
D) $34,500
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As of December 31,Frappe Company has a balance of $5,000 in accounts receivable.Of this amount,$500 is past due and the remainder is not yet due.Frappe has a credit balance of $45 in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.Frappe Company estimates its bad debt losses using the aging of receivables method,with estimated bad debt loss rates equal to 1% of accounts not yet due and 10% of past due accounts.How will the Bad Debt Expense account be included in the required adjusting journal entry at year-end?
A) Debit of $95
B) Credit of $95
C) Debit of $50
D) Credit of $50
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 230
Related Exams